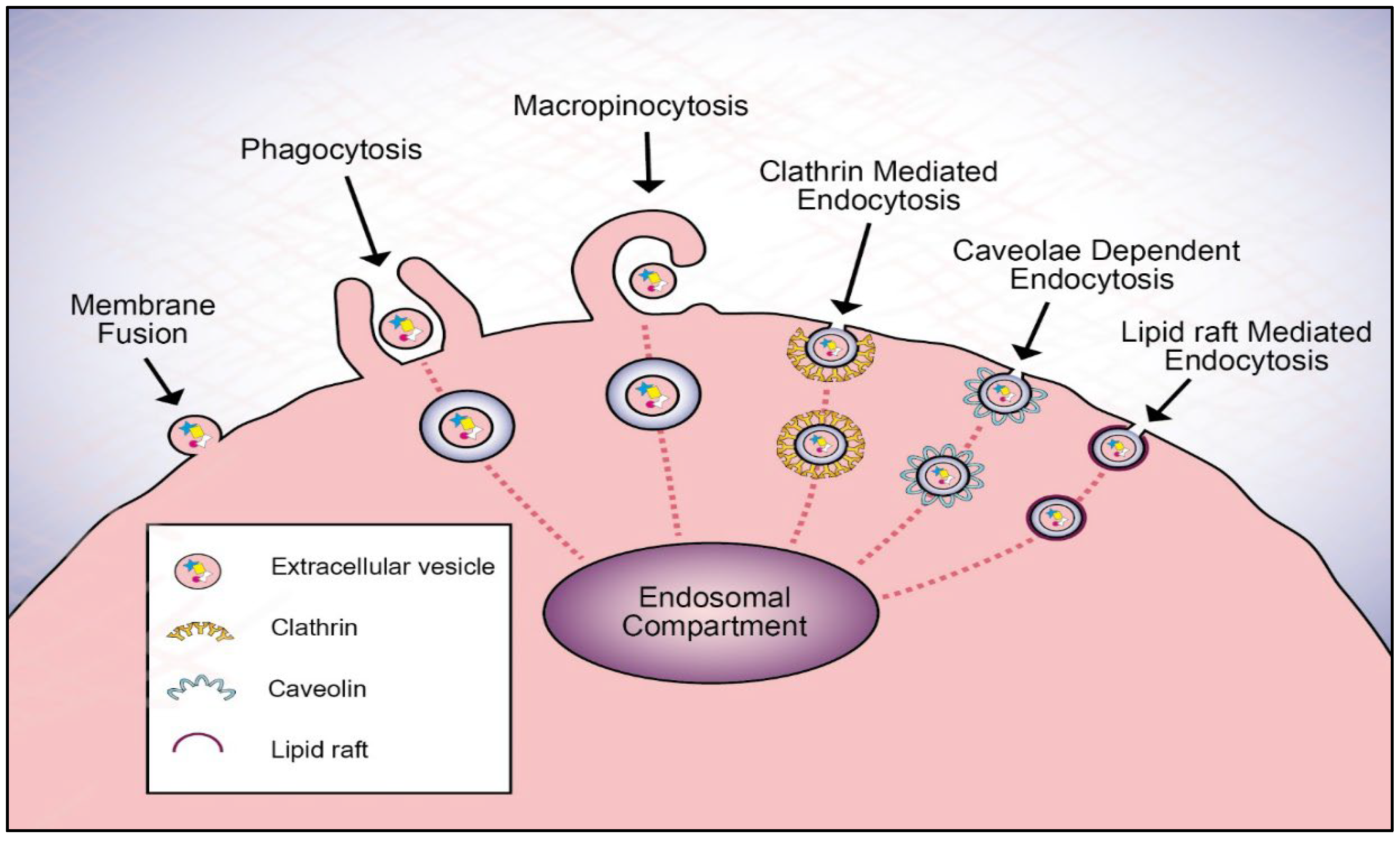
The complex world of how cells connect has made extracellular vesicles (EVs) very important for keeping our body’s systems working together smoothly. These tiny, membrane-bound particles are released by almost all types of cells and play a key role in making it possible for cells to talk to each other. They play many different roles, such as moving proteins, lipids, and genetic material, which affects many normal and pathological processes. To fully understand how complicated cellular signaling is, you need to know about the different kinds of EVs and what they do. Check out different types of extracellular vessicles to understand it more.
Different Kinds of Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular vesicles are mostly put into groups based on their size, where they come from, and how they are made. These are the main types:
- Exosomes are the tiniest EVs. Their width is usually between 30 and 150 nanometers. They come from the membranes of endosomes budding inward, making multivesicular bodies that join with the plasma membrane to send exosomes into the space outside of cells.
- The biggest EVs are apoptotic bodies, which are usually between 1 and 5 micrometers in size. They are released when a cell dies on its own, a process called apoptosis, and they contain organelles and broken cells.
What They Do in Cellular Communication
Extracellular vesicles are very important for cell signaling in a number of ways:
- Molecular Transport: EVs make it easier for proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids to move between cells, which changes how target cells behave and work.
- Immune Response Modulation: EVs can change immune responses by carrying antigens and other immune-related chemicals. Depending on the situation, they can either make immune responses stronger or weaker.
- Disease Progression: When there is a disease, like cancer, EVs can send malignant factors to nearby cells, which helps the tumor grow and spread.
- Repair and Regeneration of Tissues: EVs made from stem cells have been shown to help repair and regeneration of tissues by sending growth factors and other chemicals that help tissues grow again.
Extracellular vesicles are an important part of the complicated network of how cells talk to each other and affect many healthy and unhealthy processes. The fact that they can move molecular cargo between cells shows how important they are for keeping cells in balance and coordinating reactions to different stimuli. Knowing about different types of extracellular vesicles is important.